你在一个城市里,城市由 n 个路口组成,路口编号为 0 到 n - 1 ,某些路口之间有 双向 道路。输入保证你可以从任意路口出发到达其他任意路口,且任意两个路口之间最多有一条路。
给你一个整数 n 和二维整数数组 roads ,其中 roads[i] = [ui, vi, timei] 表示在路口 ui 和 vi 之间有一条需要花费 timei 时间才能通过的道路。你想知道花费 最少时间 从路口 0 出发到达路口 n - 1 的方案数。
请返回花费 最少时间 到达目的地的 路径数目 。由于答案可能很大,将结果对 109 + 7 取余 后返回。
示例 1:
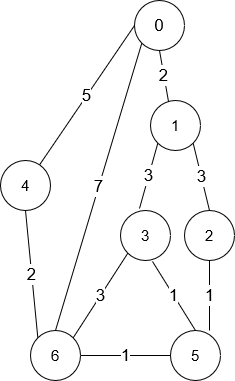
输入:n = 7, roads = [[0,6,7],[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3,3],[6,3,3],[3,5,1],[6,5,1],[2,5,1],[0,4,5],[4,6,2]]
输出:4
解释:从路口 0 出发到路口 6 花费的最少时间是 7 分钟。
四条花费 7 分钟的路径分别为:
- 0 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 4 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 2 ➝ 5 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 3 ➝ 5 ➝ 6示例 2:
输入:n = 2, roads = [[1,0,10]]
输出:1
解释:只有一条从路口 0 到路口 1 的路,花费 10 分钟。提示:
1 <= n <= 200n - 1 <= roads.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2roads[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi <= n - 11 <= timei <= 109ui != vi- 任意两个路口之间至多有一条路。
- 从任意路口出发,你能够到达其他任意路口。
我的答案:
class Solution {
public:
long long d[100000];
const long long mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
long long way[100000];
struct Edge{
long long x,w;
bool operator < (const Edge &v)const
{
if(x != v.x) return v.x < x;
return v.w < w;
}
};
vector<Edge> g[100000];
void dijkstra(int st){
way[0] = 1;
memset(d,0x3f,sizeof(d));
d[st] = 0;
bitset<100000> vis;
priority_queue<Edge> pq;
pq.push({st,d[st]});
while(pq.size()){
long long x = pq.top().x;
long long w = pq.top().w;
pq.pop();
// if(vis[x])continue;
// vis[x]=true;
if (w > d[x]) {
continue;
}
for(auto &[y,w]:g[x]){
if(d[y]>d[x]+w){
d[y] = d[x] + w;
way[y] = way[x];
pq.push({y,d[y]});
}
else if(d[y] == d[x]+w){
way[y] = (way[x]+way[y])%mod;
}
}
}
}
int countPaths(int n, vector<vector<int>>& roads) {
for(auto &i :roads){
if(i[0]!=i[1]){
g[i[0]].push_back({i[1],i[2]});
g[i[1]].push_back({i[0],i[2]});
}
}
dijkstra(0);
return way[n-1];
}
};标答:
class Solution {
public:
int countPaths(int n, vector<vector<int>> &roads) {
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> g(n); // 邻接表
for (auto &r : roads) {
int x = r[0], y = r[1], d = r[2];
g[x].emplace_back(y, d);
g[y].emplace_back(x, d);
}
vector<long long> dis(n, LLONG_MAX);
dis[0] = 0;
vector<int> f(n);
f[0] = 1;
priority_queue<pair<long long, int>, vector<pair<long long, int>>, greater<>> pq;
pq.emplace(0, 0);
while (true) {
auto [dx, x] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (x == n - 1) {
// 不可能找到比 dis[n-1] 更短,或者一样短的最短路了(注意本题边权都是正数)
return f[n - 1];
}
if (dx > dis[x]) {
continue;
}
for (auto &[y, d] : g[x]) { // 尝试更新 x 的邻居的最短路
long long new_dis = dx + d;
if (new_dis < dis[y]) {
// 就目前来说,最短路必须经过 x
dis[y] = new_dis;
f[y] = f[x];
pq.emplace(new_dis, y);
} else if (new_dis == dis[y]) {
// 和之前求的最短路一样长
f[y] = (f[y] + f[x]) % 1'000'000'007;
}
}
}
}
};
作者:灵茶山艾府
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-ways-to-arrive-at-destination/solutions/2668041/zai-ji-suan-zui-duan-lu-de-tong-shi-dpfu-g4f3/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。我感觉没什么区别不知道为什么过不去。。。。。。
